
Sec-butyl acetate landed on the chemical scene as industrial chemistry started chasing higher outputs and purer end-products. In the past, folks working in paints and coatings stuck with simpler esters until the market kept pushing for better performance—solvents that kicked up solvency, dried quicker, and left less residue. Sec-butyl acetate delivered on these points, carving its place beside its cousins—n-butyl acetate and isobutyl acetate. Adoption took off in the mid-20th century, especially as more industries needed reliable options for dissolving, blending, and carrying chemicals in ways that would not mess up sensitive materials or stall a production line. From small batch mixing in labs to roaring chemical plants, sec-butyl acetate has shown steady growth as new uses keep popping up.
The commercial form of sec-butyl acetate comes as a colorless, flammable liquid that shows up in drums, IBCs, and road tankers. It often carries a sweet, fruity odor, signaling what many people associate with strong solvents found in adhesives or nail polish. Its chemical structure (C6H12O2) shapes its role as both a solvent and an intermediate across industries. Manufacturers pay close attention to purity—as impurities can threaten both product safety and end-use performance. Reputable suppliers invest heavily in tracking batch quality, aiming for specifications exceeding 99.5% purity where possible. Buyers count on tech sheets and labels that detail origin, shelf life, and material compatibility to minimize operational hiccups down the line.
Sec-butyl acetate boils at 112–114°C and delivers a vapor pressure that enables quick evaporation without the aggressive volatility of lighter acetates. Its moderate solubility in water, along with high miscibility in organic solvents like alcohols and ketones, unlocks a host of practical uses. With a density around 0.87 g/cm³ and a low viscosity, sec-butyl acetate pours easily, supports uniform spreading and spraying, and handles blending into multi-solvent systems with less fuss than some alternatives that cause separation or jelling. Its flash point sits at 28°C—above room temperature, but still a reminder of safety when storing and working with this liquid on a factory floor.
Manufacturers stamp every shipment with batch numbers, purity percentages, and date of manufacture so buyers can trace issues or cross-check for stock rotation. Labels also show CAS number (105-46-4), UN number (1123), and enforce regulations for handling and transport—because this isn’t a chemical you want leaking around heat or ignition sources. Downstream users keep a close eye on typical impurity profiles, like residual alcohol or acids, since even small traces can set off unexpected reactions in applications from coatings to flavoring extracts used at trace levels. Product data sheets spell out recommended uses, health hazards, first aid measures, and compatible storage materials to head off corrosion or decomposition risks.
Most commercial sec-butyl acetate comes from esterification, where sec-butanol reacts with acetic acid in the presence of a strong acid like sulfuric acid. The process needs heat, careful moisture control, and removal of water to keep the reaction driving forward instead of backward. After esterification, vacuum distillation removes by-products and leftover acids, pushing purity as high as possible. Manufacturers gear their systems for maximum yield, consistent throughput, and reduced emissions—especially with stricter environmental rules kicking in. Waste recovery and responsible handling of acidic wash waters go hand-in-hand with modern production, making sure compliance and economics line up.
Sec-butyl acetate reacts as most esters do—hydrolysis with strong acids or bases cracks it into acetic acid and sec-butanol. It stands up well in conditions most paints or coatings experience, staying stable unless exposed to harsh reagents or high heat. Special conditions can drive transesterification, where swap-in alcohols reconfigure the ester, which finds use in specialty solvent production research. Compared to n-butyl and isobutyl acetates, sec-butyl acetate gives slightly different rates in hydrolysis and different interaction profiles when blended with resins or polymers, resulting in finished goods that dry at altered rates or spread with distinct leveling quality. Chemists tinker with these subtleties to squeeze out better wear, gloss, or solvent pop resistance depending on the latest customer demands.
Sec-butyl acetate answers to several aliases. Chemists often refer to it as 1-methylpropyl acetate, ethyl-1-acetate, or acetic acid sec-butyl ester. Producers stamp their own trademarks or product codes on packaging. Regulatory bodies worldwide list it under CAS 105-46-4, making it easy to match paperwork from distributors in Europe, Asia, or North America. It never hurts to check your supplier’s SDS—since mislabeling or confusion with isomers can risk compliance breaches or the wrong solvent mix, leading to costly recalls if not caught in time.
People working around sec-butyl acetate quickly learn to respect flammable liquids—no open flames, static, or sparks anywhere close. Inhalation causes headaches, dizziness, and irritation; long exposure in tight spaces makes these symptoms worse. Most plants bring in LEV systems and make PPE mandatory—gloves, goggles, and flame-resistant gear for storage or mixing. Proper spill containment and clear labeling keep minor mistakes from exploding into full-blown emergencies. Workers need ongoing training that covers fire response, first-aid for chemical exposure, and lockout rules so maintenance doesn’t lead to inadvertent release. Cross-disciplinary audits from safety officers, insurers, and environmental authorities push all players to stay sharp and honest about handling procedures.
The biggest buyers of sec-butyl acetate operate in paints, coatings, and adhesives, where it accelerates drying without leaving sticky residue or warping thin films. In automotive finishing, this solvent helps keep flow and leveling consistent—crucial for avoiding orange peel effects or fisheyes. Leather finishing plants rely on it to soften texture and set dyes more evenly. Some ink and printing sectors use it to manage drying time, ensuring crisp images that don’t bleed or feather. Niche roles crop up in fragrance blending, where its aroma fits well in fruity notes, and even in flavoring, though food use comes with strict purity standards to avoid health risks. Its role as a chemical intermediate also lets fine chemical producers convert it into specialty esters or additives for plastics, flavors, or pharmaceuticals.
Researchers keep probing where sec-butyl acetate unlocks value in coatings or solvents. Teams experiment with new blends to shave minutes from drying times or to create safer, lower-emission versions of standard products. Advances in catalysis and distillation have cut waste and raised yields, making sec-butyl acetate cheaper and greener compared to older processes. Scientists also try out novel formulations with biobased alcohols or acids to meet sustainability goals that matter more to consumers and regulators. R&D labs check how trace impurities affect everything—from gloss retention to color fastness—since a tiny formulation tweak can separate winners from the also-rans in high-volume markets. Intellectual property follows quickly, with suppliers racing to file patents on unique blends or production tweaks to keep a competitive edge.
Animal studies and occupational health surveillance flag sec-butyl acetate as a moderate hazard—short-term effects revolve mostly around irritation of eyes, nose, and lungs, and longer exposure brings risks to the nervous system. At high doses, liver and kidney stress show up in test animals, prompting occupational limits increasingly aligned with global standards. Most industrial hygiene plans pivot on air monitoring and fast leak detection, as early symptoms can escalate quickly for workers. Long-term data remain sparse, especially in low-dose, chronic settings, so health agencies keep updating safe exposure guidance as fresh studies close the knowledge gaps. For vulnerable populations—pregnant workers, those with respiratory conditions—site managers often shift tasks or upgrade containment to cut any risk of accidental exposure.
Looking ahead, sec-butyl acetate faces rising scrutiny on sustainability and emissions, much like other ester solvents. Green chemistry initiatives eye renewable feedstocks, recycling of process water, and closed-loop systems to cut down both carbon footprint and fugitive losses. Industry partners also work to create safer blends for consumer applications, especially in cosmetics or household cleaners. Digital manufacturing—using in-line sensors and real-time batch adjustments—promises greater consistency and less waste. As regulatory pressure tightens around VOCs and workplace exposure, product stewardship must jump ahead with transparent labeling, open research, and collaboration. The chemical’s versatility and robust science base give it a strong shot to stick around, provided stakeholders keep innovating, reformulating, and respecting the risks that come with such a powerhouse solvent.
Sec-butyl acetate sounds complicated, but it turns out this chemical quietly influences a lot of finished goods in everyday life. At its core, it’s a solvent. Solvents help mix, thin, dissolve, and spread other substances. Most people notice sec-butyl acetate’s handiwork when paint dries smoothly on the wall or when certain inks stick to packaging without streaks. It delivers crisp results and evaporates without a heavy chemical smell.
If you’ve ever painted furniture or even a room, you might have looked for a finish that dries quickly and doesn’t leave tracks. Sec-butyl acetate helps with that. This solvent persuades resins and pigments to stay evenly mixed. It gives enough time to apply paint before it dries but doesn’t drag out the job. Furniture, vehicles, and metal structures all benefit from these qualities. Large-scale paint makers use sec-butyl acetate because it strikes the right balance—neither too slow nor too fast.
Many consumer goods reach shelves looking sharp thanks to sec-butyl acetate. During label design and printing, companies want inks that won’t smudge or fade. The chemical works behind the scenes, letting printing presses run faster since inks set more reliably on surfaces like plastic, foil, or cardboard. As a result, supermarket shelves look organized, not messy or inconsistent. Printers trust it because clean labeling means fewer errors, less rework, and better safety for the people using those packaged products.
Manufacturers aren’t just worried about looks; they need to protect sensitive gear, too. When securing insulation on wires or applying coatings to circuit boards, small mistakes add up. The electronics industry values sec-butyl acetate because it won’t corrode metal or melt plastics at effective doses. It cleans and preps surfaces so they stay responsive and reliable—think of all the tiny circuit boards inside computers, chargers, and phones.
Sec-butyl acetate isn’t just for factories. Many perfumes, nail polish removers, and colognes count on it to spread their scents quickly and evenly. It’s strong enough to dissolve perfume oils but gentle enough not to overpower the product. I’ve noticed my favorite aftershave feels lighter and dries up quickly; it turns out sec-butyl acetate lets delicate scents linger without leaving residue.
Using strong solvents calls for solid training and careful handling. Workers in paint shops and printing, for instance, keep an eye on proper ventilation because high exposure leads to headaches, skin irritation, or worse. Regulators such as the EPA and OSHA track safe limits to shield both workers and neighbors from harm. Wearing gloves and goggles, reading labels, disposing of leftover solvents properly, and sticking to approved ventilation can prevent short- and long-term health issues.
The world’s attention is shifting toward greener practices. Although sec-butyl acetate performs well, many labs and factories look for less-toxic options and ways to recycle solvents. Switching to water-based paints or new bio-derived ingredients won’t happen overnight. Manufacturers and environmental experts are teaming up to test processes that reduce emissions and handle waste more responsibly. The chemistry world hasn’t found a perfect replacement yet, but every step towards less pollution and safer jobs counts.
Sec-butyl acetate’s value stretches from painted toys to high-end electronics and personal care supplies. Its quiet versatility keeps factories humming, shops stocked, and homes looking sharp.Sec-butyl acetate pops up in industries ranging from paints and coatings to labs and adhesives. Each time I set foot in a workshop or visit a small manufacturing outfit, the topic of chemical safety lands front and center. Employees handle solvents like sec-butyl acetate all the time, sometimes as casually as water. The smell is sharp and sweet, almost like nail polish remover—reminding you it’s more than just a harmless splash.
Safety data sheets always warn that sec-butyl acetate can irritate skin, eyes, and lungs. My first week mixing solutions in a paint lab, splashes taught me that gloves and goggles aren’t accessories — they’re a must. The liquid stings on contact and the vapors make your nose wrinkle. Eating a sandwich in the same room would’ve been a mistake. It evaporates fast. Breathing the fumes for long periods led to headaches and dizziness, both for me and coworkers. These experiences turned theory into real caution.
Workplace studies back this up. The US National Library of Medicine notes sec-butyl acetate has moderate toxicity—unlike more notorious chemicals, but enough that exposure rules apply. OSHA sets exposure limits for a reason: repeated or heavy contact raises the risk for more serious effects. The liver and nervous system take the brunt over months or years of sloppy habits. Right away, the signs are tough to ignore: red skin, watery eyes, a rasp in your voice after a busy shift.
Small shops and garages often believe ventilation is a luxury. I once saw a friend touching up auto panels in a closed garage; it doesn’t take long in that stuffy air before headaches sneak up and coordination drops. Label warnings can blend into the clutter, ignored by workers eager to finish fast. Sometimes, supervisors skip fit-testing for respirators and eye protection feels optional. It only takes one slip, one splash in the face, to reconsider.
Sec-butyl acetate won’t spare you just because yesterday passed without trouble. Keeping containers sealed, using fans or open windows, and respecting glove changes become second nature with good training. Sometimes it means slowing down. Proper ventilation pulls fumes away. Disposable nitrile gloves handle most spills, but swapping them out at the first sign of damage or if fingers feel cold keeps your hands safe. Face shields add comfort for mixing or pouring.
Switching chemicals isn’t always possible, but a conversation about less volatile solvents can improve safety, especially for businesses with low budgets. Some companies lean into “green” alternatives, but those products need close scrutiny too. Just because it’s newer doesn’t guarantee safety. Checking reliable data sheets, not just trusting a marketing label, makes the difference. Peer-reviewed research and manufacturer transparency help fill in the gaps for workers making choices that impact their bodies every day.
The lessons come fast in environments where messes and shortcuts meet. Each cough and rash became my own safety training. Over time, choosing good habits over hasty jobs gives everyone a better chance to go home healthy. Knowledge, not just equipment, builds a safer workspace—something worth carrying into every job around chemicals like sec-butyl acetate.
Sec-butyl acetate stands out as a useful solvent in paints, coatings, and chemical synthesis. Its strong, somewhat fruity smell makes its presence clear, and its flammable nature keeps safety at the forefront. Neatly storing this liquid isn’t just a rule to follow; it’s about keeping workplaces safe and avoiding costly incidents.
Anyone who has worked with flammable solvents knows that heat invites risk. Sec-butyl acetate prefers a well-ventilated, cool area, far from direct sunlight and sources of ignition. Temperatures over 30°C make vapors settle in the air, creating a real explosion hazard. I once saw a small warehouse where barrels sweated in the summer heat. A single spark from a nearby tool could easily have sparked disaster. Smart operators keep solvents away from hot equipment, welding areas, or even something as simple as a light with old wiring.
Fresh air moves vapors out and brings clean air in. Stagnant air lets fumes build up. Inhaling high concentrations can bring headaches or drowsiness. I keep in mind stories shared by old-timers in the field who sometimes tried to “air out” storage areas after the fact—making sure there’s always proper ventilation is better than any band-aid fix later.
Steel drums with tight-fitting lids guard against leaks and evaporation, and they keep air or moisture from getting in. Sec-butyl acetate reacts with water and acids, so only compatible materials belong nearby. I’ve seen that routine checks for visible corrosion or dents on storage barrels pay off—small issues can grow quickly with chemicals like these.
A clear, tough label never seems flashy, but it matters. No one wants to play guessing games about what’s in an unmarked drum during an emergency. Stickers that list chemical name, hazards, and date of receipt ring especially helpful if an inspector shows up or a new worker rotates in.
Grouping chemicals is no time for improvisation. Sec-butyl acetate never belongs near oxidizers, strong acids, or bases. Mixing by accident, even from a drip or splash, could lead to violent reactions—or as I once learned in university, a chemical cloud that sends everyone out of the lab for hours.
Every storage plan finds its backbone in preparation. Spill kits stand close. Fire extinguishers rated for flammable liquids stay within easy reach, not buried in a locked cabinet. Absorbent pads, goggles, and gloves sit where they can be grabbed in seconds. I’ve noticed that time spent on regular drills isn’t wasted. Hands know what to reach for, and confusion drops away in those early tense moments of a spill.
Companies who keep up on training and keep their systems simple earn trust from both employees and regulators. Good practice? Recording inventory movements, inspecting storage at set intervals, using “first in, first out” so no barrel sits forgotten on a back shelf.
The rules may seem strict, but every one traces back to real accidents and lessons learned. Approaching sec-butyl acetate storage with a wide view of safety, clear communication, strong labeling, and a plan anyone could follow proves its worth every day.
In everyday tasks—painting a room, stripping off old varnish, or even sitting near a freshly glued floor—sec-butyl acetate might be hanging out in the air. This clear, colorless liquid carries a sweet, fruity smell that tends to spill over easily in poorly ventilated spaces. At room temperature, it acts like many other organic solvents, flowing quickly and evaporating faster than water left out on a summer day.
Sec-butyl acetate boils at about 112 degrees Celsius, which means it stays liquid in most indoor settings but runs away as soon as things heat up. Spill a little, and that gentle aroma tells you evaporation isn't far behind. Its density hovers at 0.87 grams per cubic centimeter, so it won’t sink in water, but rather form a thin layer floating at the top. It doesn’t mix much with water either—just over two grams dissolve into a liter at room temperature. Since it’s lighter than water and resists blending, runoff or improper disposal can lead to a sheen on streams or storage ponds.
Storing this solvent calls for care. Its flashpoint sits around 28 degrees Celsius, meaning a spark or open flame nearby can kick up a fire faster than many folks expect. You’ll often find it in metal cans or drums far away from ignition sources in industrial settings. Workers keep it tightly capped, not just to keep it from evaporating, but to cut down fire risk.
Chemically, sec-butyl acetate falls into the ester family. This means it comes from a reaction between a butanol and acetic acid. Like other esters, it breaks down if mixed with strong acids or bases, giving off alcohol and acid as byproducts. In practice, this instability means storage containers shouldn’t see much sunlight, high heat, or rough chemical company. At work, that translates to controlled storage conditions, solid ventilation, and spill kits within arm’s reach.
Sec-butyl acetate doesn’t show up in the news, yet it plays a quiet role in making things smoother and shinier. It thins out inks and lacquers, helps dissolve adhesives, and makes coatings spread nicely. As a worker who spent time in an auto body shop, I’ve seen what happens if you skip gloves or a mask. Hands can dry out and crack, and the smell can leave a headache behind after a few hours. NIOSH considers exposure of more than 200 ppm over eight hours as unsafe. In small spaces, vapors can reach that level much quicker than most folks imagine.
The Environmental Protection Agency has flagged sec-butyl acetate as volatile and not biodegradable in the short term. That means spills or dumps won’t disappear fast and could impact waterways or soil. The fix comes through tight handling procedures, using less toxic substitutes when possible, and good training for everyone involved, from the loading dock to the lab bench. Wearing the right gloves and respirators, and recycling solvents when practical, can cut back on health and environmental worry.
Sec-butyl acetate offers more than just convenience on a product label—it raises plenty of safety, health, and environmental concerns. In years spent handling solvents, I’ve learned that knowing what’s in the can and how it behaves makes the difference between safe work and a serious setback. Reliable labels, ventilation, and up-to-date chemical training go a long way. With strict controls and a little common sense, the benefits don’t have to come at a hidden cost.
Ask anyone working in a lab or a factory about sec-butyl acetate, and you’ll usually hear, “Yeah, it’s flammable. Handle with care.” Sounds simple, but curiosity goes beyond a safety label. Why do folks need to know about the flammability of sec-butyl acetate anyway? At the root, it’s about keeping workplaces, schools, and even our communities safe.
Sec-butyl acetate crops up a lot, whether it’s for coatings, cleaning solvents, or as part of chemical synthesis. The story always starts with its properties. Sec-butyl acetate carries a flash point of around 22°C (72°F). This number isn’t just technical chatter—flash point refers to the lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapor to ignite in air. At this level, a forgotten beaker or open drum can release enough vapor to become an explosion risk on a warm day. So, yes, sec-butyl acetate is flammable. There’s no way to sugarcoat this aspect, and history proves the need for vigilance. Warehouse fires caused by improper handling of similar solvents have cost companies millions and left toxic plumes in their wake.
Nobody wants to see that happen. Speaking from experience, it only takes a momentary lapse—somebody opens a drum near a welding station or skips checking for a spark-proof fan in a cramped storage closet. Every year, there are OSHA reports about fires started from solvents like this one, showing up in places where regulations seemed like background noise until something went wrong.
Sec-butyl acetate's molecular structure—an ester with a butyl side chain—doesn’t make it an outlier. Plenty of acetates catch fire without much effort. Unlike water-based solutions, flammable liquids form an invisible hazard; vapor lingers close to the ground, ready to ignite with just a stray spark or static charge.
There’s an urge to shrug this off and lean on modern ventilation or fire suppression systems. Fact remains, most fires start on the human side—mixing containers, skimping on personal protective equipment, working in cramped quarters where vapor concentrations can spike. Simple safety routines often get lost in the daily shuffle, especially under deadlines or budget crunches.
Nobody has to reinvent safety. Keep sec-butyl acetate stored in clearly labeled flammable cabinets. Minimize quantities in use, and never let vapor accumulate in closed spaces. Keep ignition sources far away. Workers need real training—not just a rushed walk-through—about spill protocols and emergency response. I’ve seen firsthand how a dry chemical fire extinguisher and a well-placed safety shower can turn a bad day into a manageable one.
Facilities benefit from reviews by external safety consultants—fresh eyes spot those accidental near-misses that go unseen during busy shifts. For shipping and storage, compliance with transportation rules (like those from the Department of Transportation and the International Air Transport Association) keeps incidents at bay. Local fire marshals provide another layer of accountability, and their advice shouldn’t land in the suggestion box.
For classrooms, simple demonstrations—like using vapor detectors or controlled ignition of solvent samples—drive home the lesson better than any textbook. Anyone can describe a fire hazard, but watching vapors flare up changes how seriously people approach flammable chemicals.
Sec-butyl acetate won’t vanish from shelves anytime soon. Choosing alternatives or engineering controls often costs more, but it beats the price of a single fire or health scare. Whether it’s ongoing training, engineering upgrades, or basic housekeeping, treating flammables with respect keeps people safe—and that’s a lesson worth repeating.
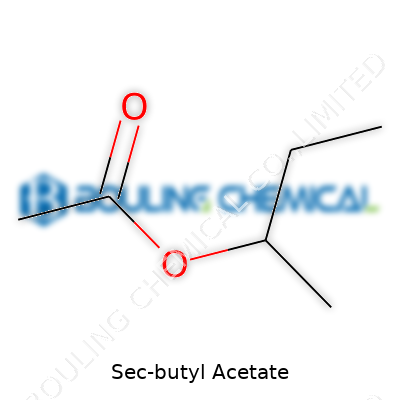
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | Butan-2-yl acetate |
| Other names |
Acetic acid, sec-butyl ester
2-Butyl acetate sec-Butyl ethanoate 1-Methylpropyl acetate Acetic acid sec-butyl ester |
| Pronunciation | /ˌsɛkˈbjuːtɪl ˈæsɪteɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 105-46-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1361112 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8733 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL15939 |
| ChemSpider | 56395 |
| DrugBank | DB14003 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.653 |
| EC Number | 123-86-4 |
| Gmelin Reference | 6077 |
| KEGG | C19534 |
| MeSH | D013494 |
| PubChem CID | 8007 |
| RTECS number | AJ3675000 |
| UNII | 73R9A3EW6J |
| UN number | UN1123 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Odor | Pleasant, fruity, banana-like |
| Density | 0.870 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | 6 g/L |
| log P | 1.78 |
| Vapor pressure | 17 mmHg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ 25 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb: 15.86 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -7.68×10⁻⁶ |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.3940 |
| Viscosity | 1.0 mPa·s (at 25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 3.97 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 265.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -471.8 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3733.8 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H336, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P261, P271, P280, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| Flash point | 73°F (23°C) |
| Autoignition temperature | “426°C (799°F)” |
| Explosive limits | 1.7% - 8.0% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): 13,100 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): 13,100 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| NIOSH | SA 3325000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 200 ppm |
| REL (Recommended) | 200 ppm |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 2000 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
n-Butyl acetate
Isobutyl acetate tert-Butyl acetate sec-Butanol Acetic acid |